Do you have a trouble to find 'admet metathesis'? You will find all the information on this section.
Table of contents
- Admet metathesis in 2021
- Admet properties
- Admet polymerization
- History of olefin metathesis
- What is an acyclic diene
- Admet mechanism
- Admet drug discovery
- Admet polymerization review
Admet metathesis in 2021
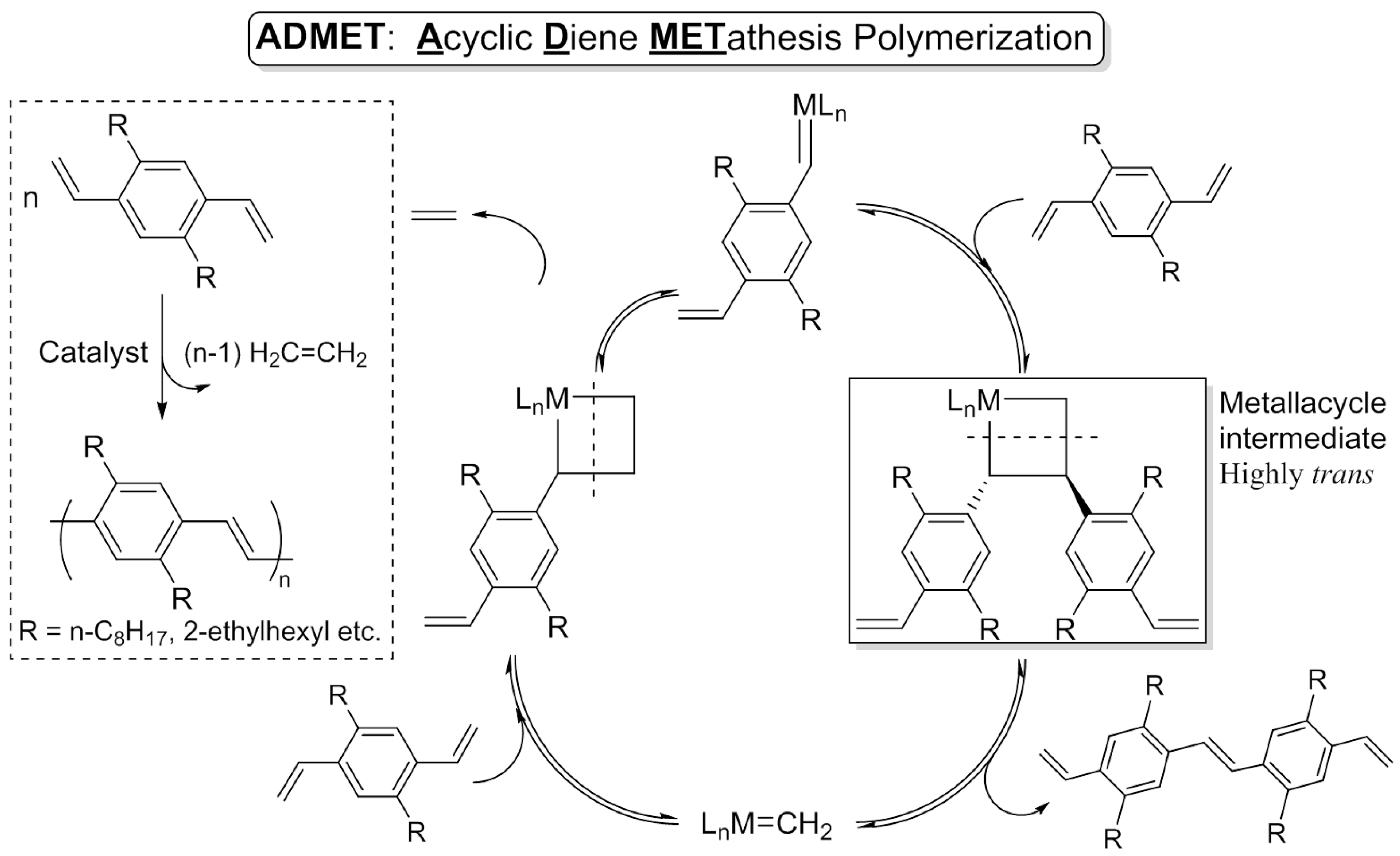 This picture representes admet metathesis.
This picture representes admet metathesis.
Admet properties
 This image shows Admet properties.
This image shows Admet properties.
Admet polymerization
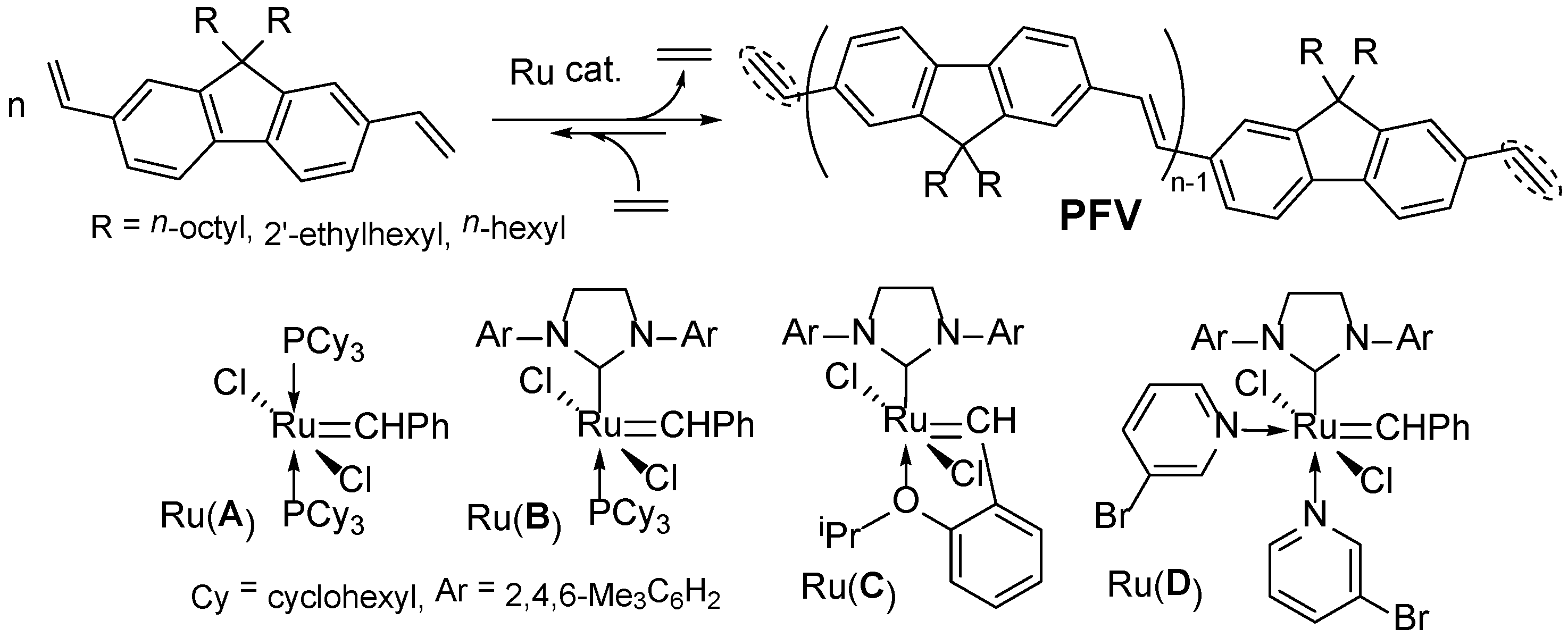 This image shows Admet polymerization.
This image shows Admet polymerization.
History of olefin metathesis
 This picture shows History of olefin metathesis.
This picture shows History of olefin metathesis.
What is an acyclic diene
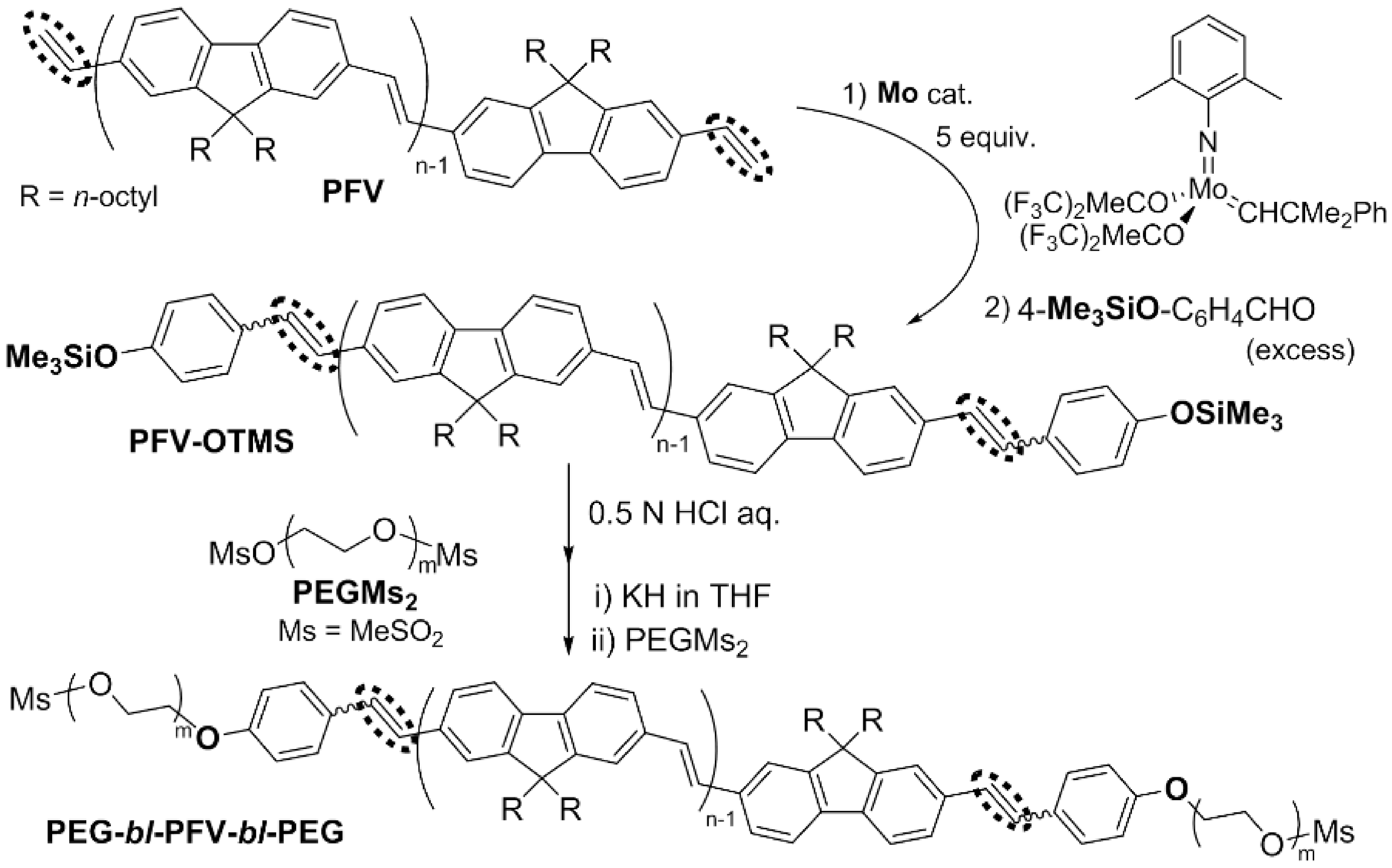 This picture illustrates What is an acyclic diene.
This picture illustrates What is an acyclic diene.
Admet mechanism
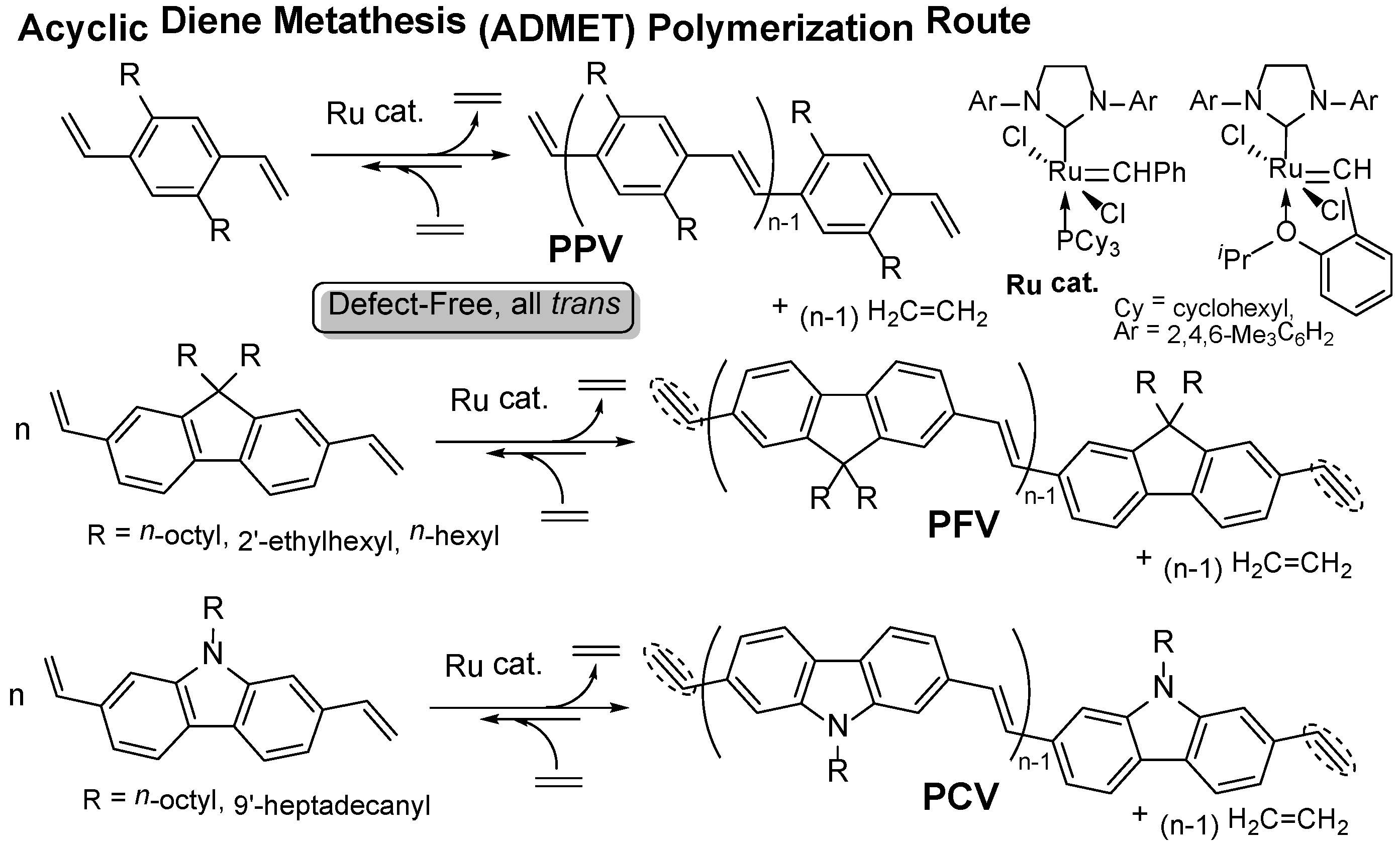 This picture illustrates Admet mechanism.
This picture illustrates Admet mechanism.
Admet drug discovery
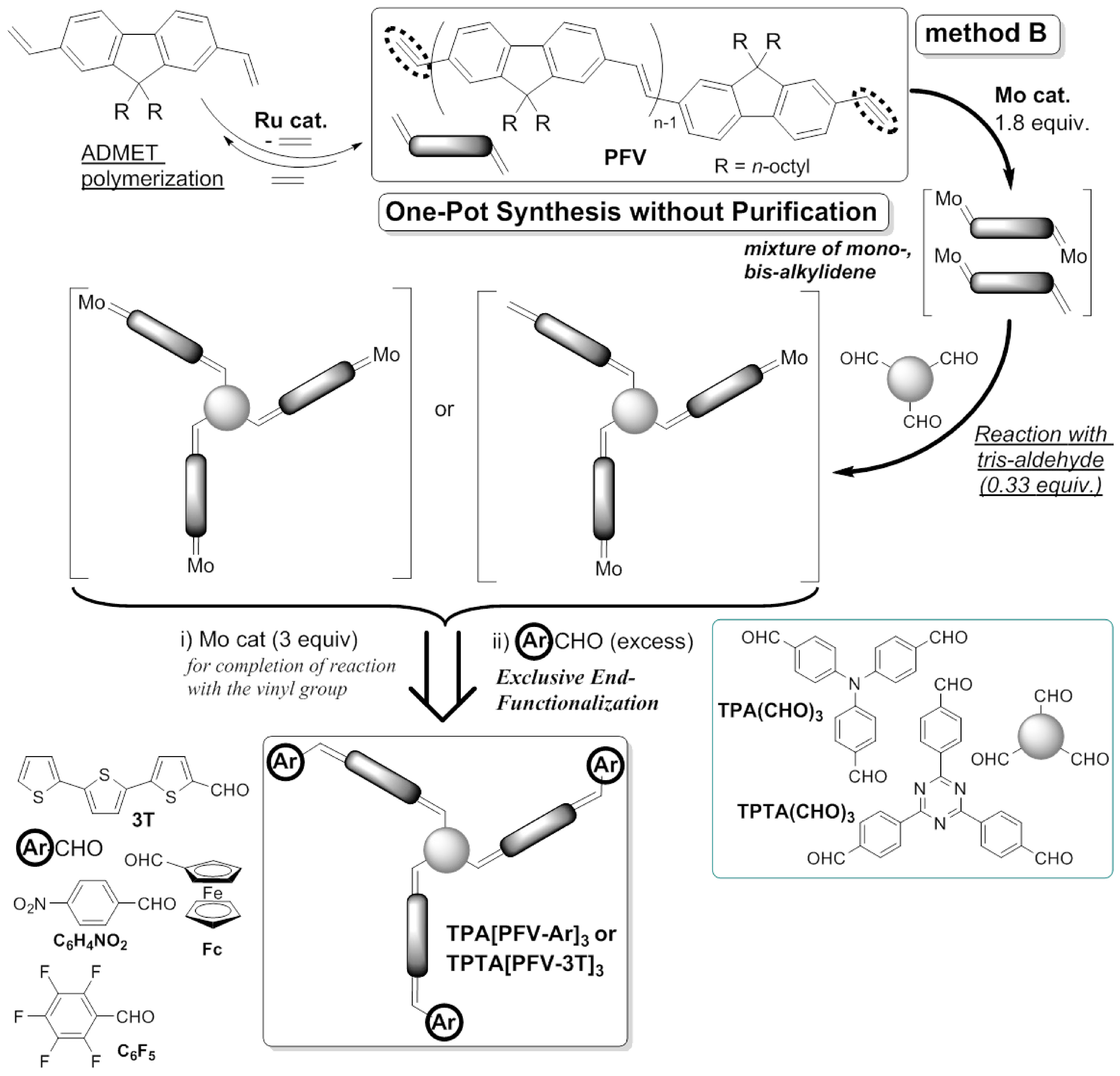 This picture illustrates Admet drug discovery.
This picture illustrates Admet drug discovery.
Admet polymerization review
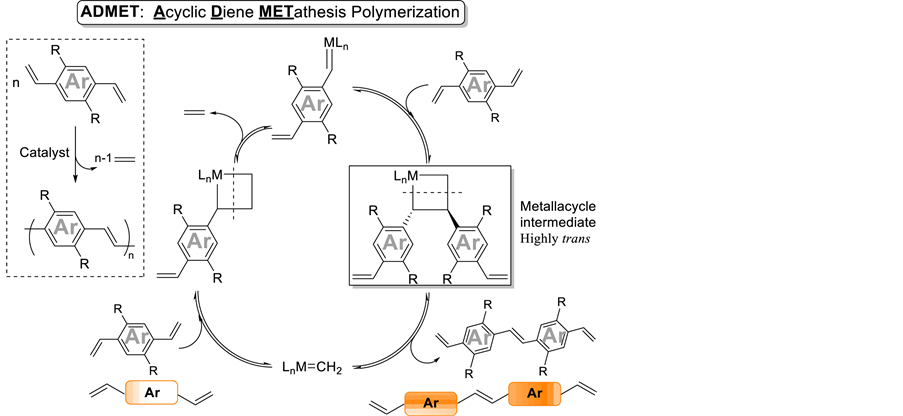 This image shows Admet polymerization review.
This image shows Admet polymerization review.
Why are olefins used in cross metathesis and ring closing metathesis?
Cross metathesis and ring-closing metathesis are driven by the entropically favored evolution of ethylene or propylene, which can be removed from the system because they are gases. Because of this CM and RCM reactions often use alpha-olefins.
Why is ADMET reaction conducted in neat monomer?
ADMET reactions are typically conducted highly concentrated or in neat monomer, both to help drive the polymerization equilibrium and to limit the formation of undesired cyclic oligomers by ring-closing metathesis mechanisms (“backbiting”).
How is ADMET used in the synthesis of polymers?
ADMET has been applied in the synthesis of a variety of polymers. Because of the higher degree of control in ADMET than in traditional radical polymerizations, it has been used to synthesize model polymers that would otherwise be difficult to prepare.
What can be produced by acyclic diene metathesis?
Acyclic Diene Metathesis (ADMET) uses metathesis of terminal dienes to produce linear polymers and ethylene. Because ADMET is actually a variation on cross-metathesis, the process is reversible, and ethylene must be removed to drive the polymerization to completion.
Last Update: Oct 2021